Page title, title tag, meta title, SEO title, some people call this different, but no matter what you’re calling it, this HTML element and its content can significantly influence your organic rankings in Google.
While meta descriptions don’t directly influence your rankings, the title tag is one of the most important factors that Google uses to rank you on their search results page.
If you want to learn what they are and how to create one that will help you with your organic rankings in search engines, you’ve come to the right place, as this guide will cover it all.
Table of Contents
- What are SEO title tags? (and why are they important?)
- Title tags appear in search results
- Title tags appear in browser tabs
- Title tags appear on social media
- What's the difference between title tags and H1-tags?
- How to write the perfect SEO title tag?
- Step 1. Find your primary keyword to target
- Step 2. Find the long-tail variations of your primary keyword
- Step 3. Draft your title tag
- Step 4. Optimize by looking at what's unique about your content
- What is the ideal title tag length?
- Title tag auto-generation: how to craft perfect titles tags for product and category pages using boiler templates
- Why is Google rewriting my title tags?
- 1. Google thinks that your title tag isn't great at all
- 2. Google thinks there's a more suitable title tag for a particular query
- 3. Google is looking at the anchor text of your inbound links to determine topic
- How can I make stop Google from rewriting my title tags?
What are SEO title tags? (and why are they important?)
The title tag, or page title, is a crucial element in your website’s HTML code. It is located in the <head> section and displays as the clickable headline in search engine results and browser tabs.
Although it might seem small and insignificant, a title tag is more important than you might think.
Just like the title of a movie catches your attention, the title tag on a page is the first thing people see in the search engine results pages (SERPs) and invites the reader over to your website probably the most.
A well-crafted title tag improves user experience and search engine optimization by summarizing the page’s content in a very condensed matter.
They are important for usability and Search Engine Optimization (SEO) and must be short, precise, and descriptive.
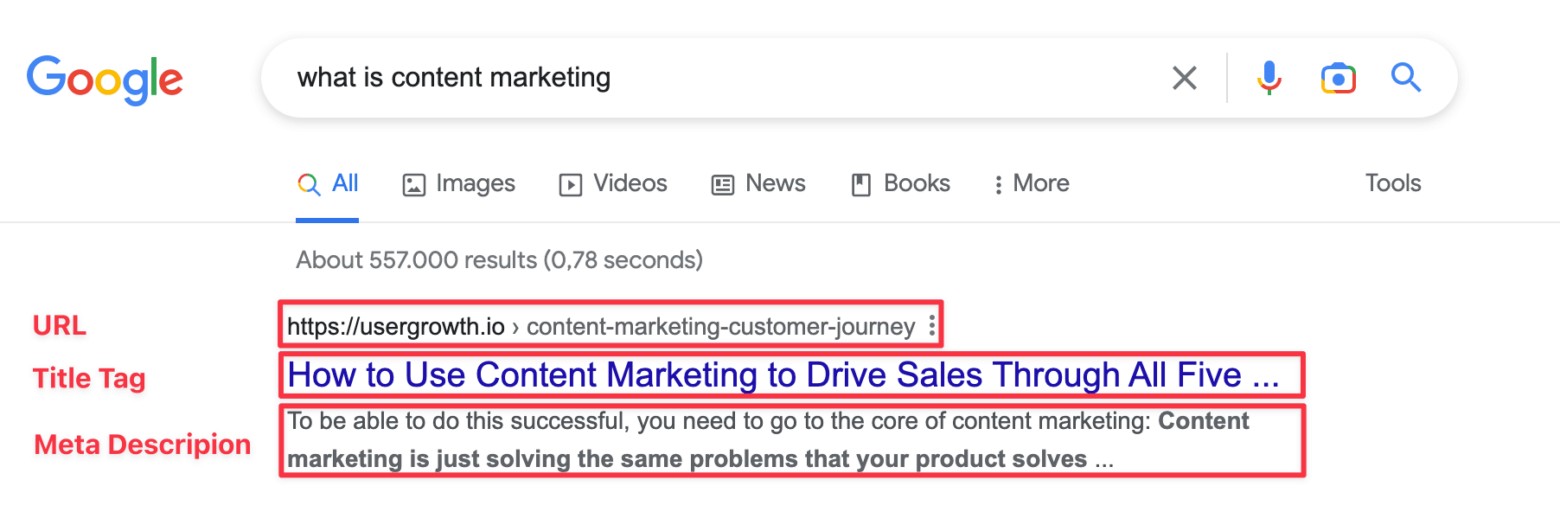
So what is a title tag? Well, a title is something that…
Title tags appear in search results
When a user searches for something on Google, the title tag is the clickable headline that appears in the search results. It should be clear and concise and give users a good idea of what they can expect to find on the webpage.
Title tags appear in browser tabs
When a user has multiple tabs open, the title tag is what appears in the tab. This helps users navigate between tabs and find the one they’re looking for.
Title tags appear on social media
When a link is shared on social media, the title tag creates the post. It should provide important context for the post and clarify what the link is about.
And that is just how they appear, so to learn all about them. Let’s dive into title tags, so you can write better title tags and start bringing in more traffic for your business.
What’s the difference between title tags and H1-tags?
While they may appear similar, they serve completely different purposes and impact your website’s visibility differently.
Title tags, as seen in the SERPs and when your content is shared on other platforms, are the main identifiers of your web page’s content. H1 tags, on the other hand, serve as the main header and title on the actual page.
It’s common for many websites to have a similar copy for their title tags and H1 tags, which may contribute to confusion. However, it’s a standard practice that helps with clarity and consistency for users. When users click through from the SERPs, they expect to see a similar or the same title as those listed in the SERPs.

It’s important not to confuse the H1 tag with the title that appears in the browser tab, as that is the title tag.
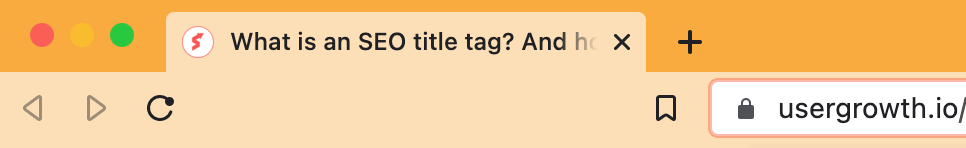
Now that you clearly understand the differences between title tags and H1 tags, it’s time to focus on creating effective and compelling title tags for your website.
Join us in the next section as we dive into the best practices for crafting an optimized title tag.
How to write the perfect SEO title tag?
Step 1. Find your primary keyword to target
While a web page never ranks just for one keyword, and it will always end up ranking for multiple keywords (so you should be optimizing your content for multiple variations, both in short-tail keywords and long-tail keywords), you should still optimize your title tag just for one main keyword.
Which one to use?
Let’s say you write an article in which you share many different SEO tips for people to help grow their business using organic traffic.
You can use a tool like SE Ranking and write down a short description of the article you create.
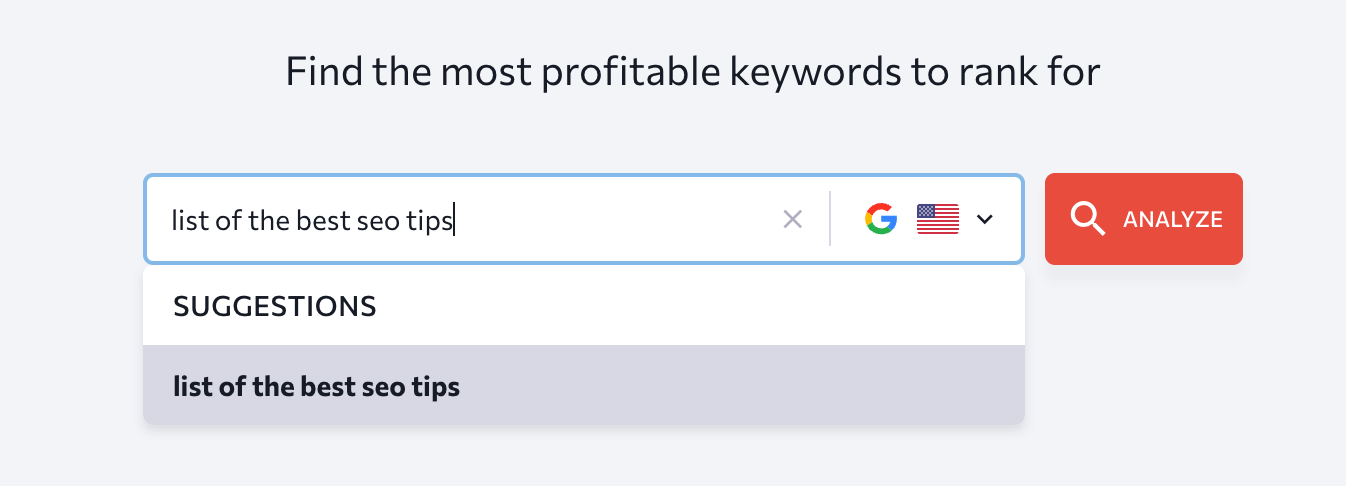
There could be times that there is almost zero search volume for your description, and even if there is, we think it is best to use the detailed report in the keyword ideas section:
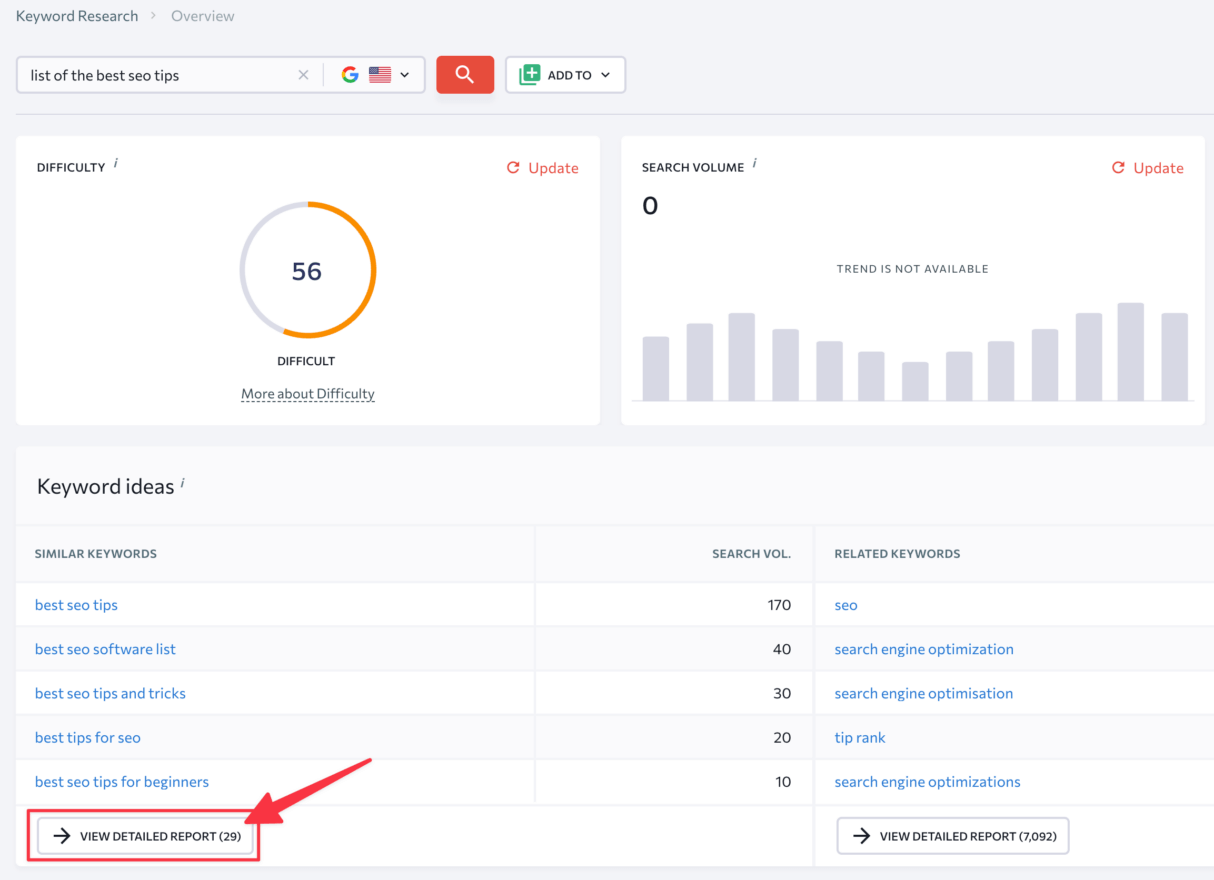
And then, finally, sort the results by search volume to see the most used keywords around the query that you entered:
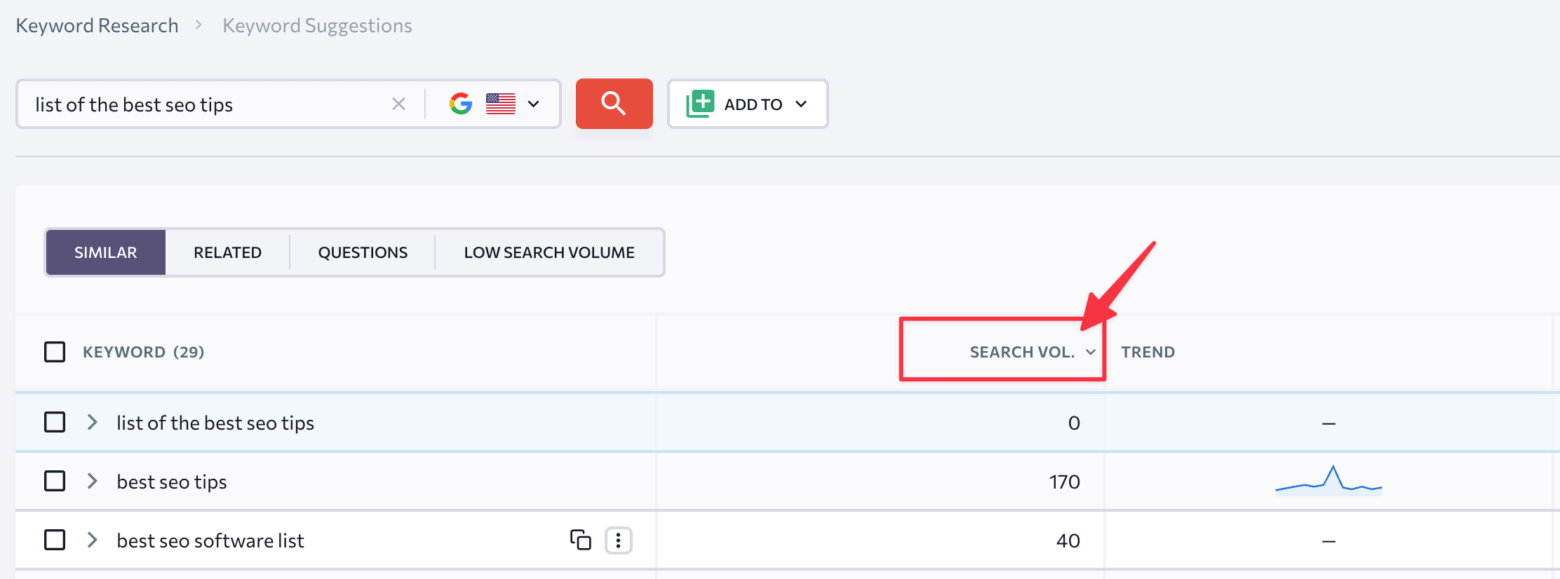
This keyword is probably the best main keyword related to the content that you’re writing.
Another way to find the main keyword for the piece of content you’ve written is to ask chatGPT: “What is the main keyword for this piece of content: “ and paste the content of your article.
For example, when pasting the content of this article, the response was:

Step 2. Find the long-tail variations of your primary keyword
While optimizing your page title for just one main keyword is best practice, it also makes sense to try to find one or two long-tail keywords.
Why?
Well, the competition is less fierce, making it easier for you to rank on the first page more quickly.
Another great reason to look at long-tail keywords is that they almost already form a sentence, so a title incorporating a long-tail keyword is a lot easier.
Step 3. Draft your title tag
Time to create your first version of your title tag! Now that you know the keyword to focus on, it’s time to sharpen your pencils and write some first variations of what could be a great title tag. The most important things to focus on here are:
- be descriptive: make sure your title accurately reflects the content of your page/post, giving readers a clear idea of what to expect.
- be concise: your title tag should be succinct, keeping it within 50-60 characters or less. As you progress through this guide, you’ll refine and tweak it, so leave room for future adjustments.
- integrate your keywords: make sure your primary keyword is included in your title tag. If feasible, include relevant long-tail variations to boost relevancy.
Step 4. Optimize by looking at what’s unique about your content
Google searches are all about finding what you’re looking for, but that “what” can vary greatly. The results people seek will depend on the nature of their query. As a content creator, it’s crucial to understand what people are searching for and ensure your page/post aligns with those desired qualities. Your title tag is your chance to make that connection and show why your content is worth clicking on.
Here are five common “qualities” to consider:
- Depth: In-depth resources are highly valued. If your content is more comprehensive than others, don’t be afraid to shout it out with phrases like “ultimate,” “complete,” “definitive,” or “step-by-step.”
- Lists: People love lists. Include a number in your title tag for list-style posts.
- Speed and Brevity: Concise, to-the-point content is in high demand. There is a reason why videos are getting smaller and smaller. Information overload is becoming a real problem. Use words like “quick,” “simple,” or “today” to entice clicks. If you offer perks like free shipping, make sure to mention that in your title tag too.
- Freshness: People want the most recent information. Use phrases like “in 2023” or “last updated” to communicate that your content is up-to-date.
- Brand: People are likelier to click results from a brand they recognize. If you have a well-known brand, make sure to include it in your title tag.
For e-commerce sites, “price” can also be a factor, so if you’re competing on cost, use terms like “cheap,” “bargain,” or “$XXX.”
But what if your page offers multiple “qualities”? Don’t overstuff your title tag. Instead, keep it natural and consider the search results that are already ranking. The top results will give you an idea of what people value. For instance, if you search “best restaurants in New York,” you’ll see that the majority of the top results are list articles. This suggests that “quantity” is what people want. On the other hand, if you search “cheap holidays,” you’ll see that price is the key factor.
When creating your title tag, always align it with the searcher’s intent. For example, if you have a post titled “75 SEO Tips that Work in 2018,” your tag aligns with a desire for up-to-date information while also offering depth and quantity.
And there you have it, a guide to crafting title tags that meet searcher needs and drive clicks. Happy ranking!
What is the ideal title tag length?
How long should a title tag be? Well Google simply offers us this advice:
Page titles should be descriptive and concise – source Google’s official title tag developer support page
To be honest, this isn’t of course a clear answer that you can work with so let’s look at some data. Currently the space that Google allocates in the search results is 568pixels wide to display the title tag.
That means a good title tag shouldn’t be longer than this space, translating in around 65 characters.
But should you really use the maximum amount of available characters or should you use less? Backlinko researched 4 million search results using the data of Semrush to figure out what will get you the best results. What seems?
Titles that are between 40-60 characters have the highest organic CTR.Click To Tweet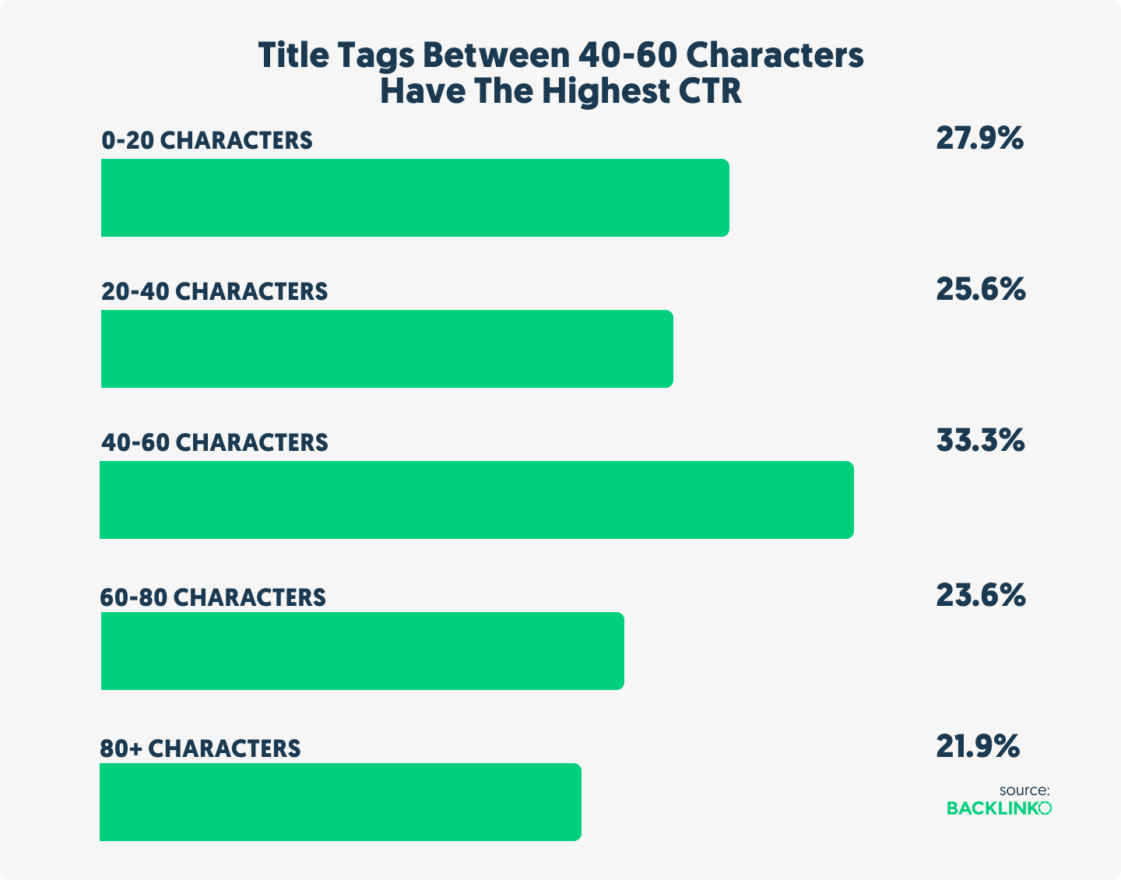
When you’re looking at individual word count, the findings where quit similiar:
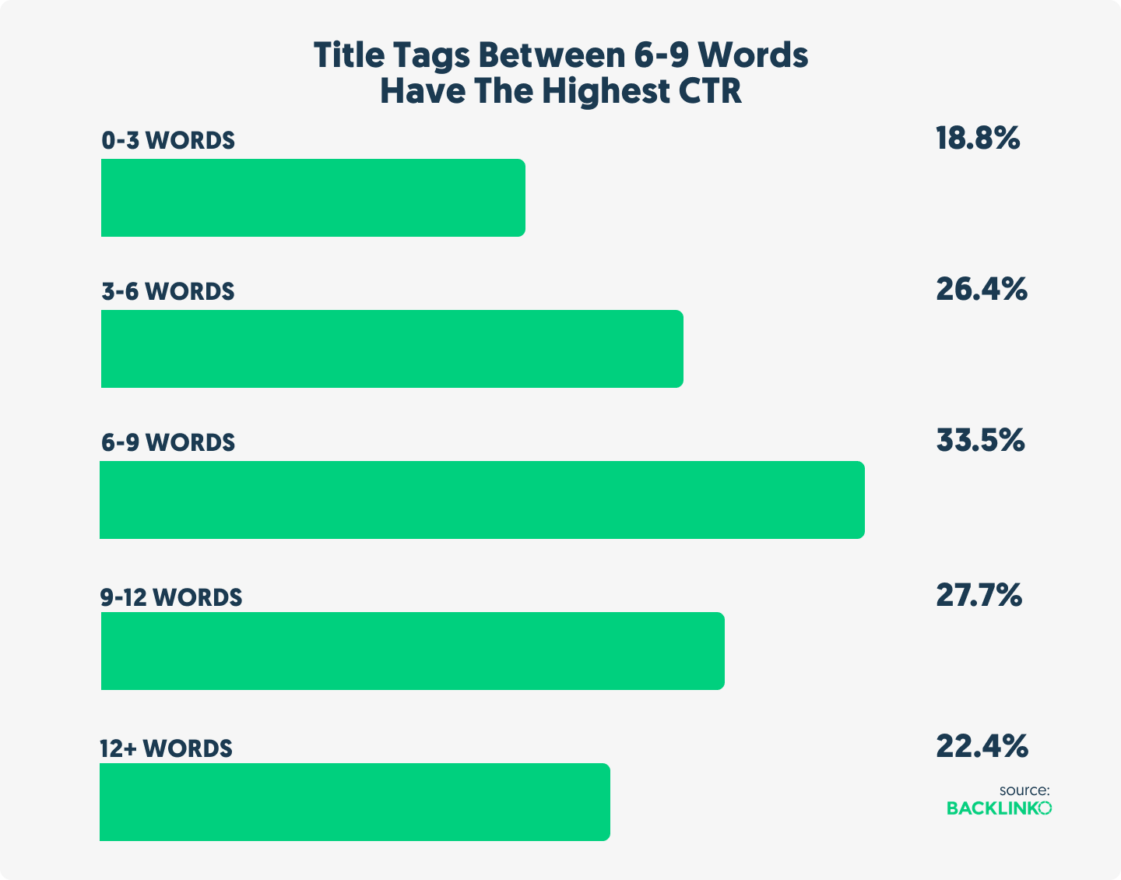
While there may be an SEO benefit of long title tags (longer titles=more keywords), this may be partially offset by a lower organic CTR. Which is also confirmed by another study done by Etsy, where they found that shorter title tags performed better than longer ones.
So try to not go over 65 characters, but even better stay somewhere between 40-60 characters for the ideal SEO title tag length.
Title tag auto-generation: how to craft perfect titles tags for product and category pages using boiler templates
When you have a website with more than just a handful of pages, like an e-commerce website, for example, the number of pages you need to create titles for can run into the thousands, maybe even millions (hello 👋 Amazon).
At a certain point, it might be more interesting to start generating these titles using a template. And sure, you might not have the same CMS as Amazon to power your e-commerce store. But there are a lot of plugins that can help you to template the title tags on your pages.
For example:
- if you use WordPress, the Yoast plugin offers a comprehensive solution with a list of custom variables you can use in meta-tags, the same for RankMath.
- if you use Joomla, you can use the Tag Meta plugin
- or if you use Magento, it should handle title tags for the category and product pages quite well out of the box. If you need more functionality, you can try Magento’s extension.
But that is just the technical part. How to structure your title?
The following are some best practices for auto-generated title tags for product pages:
Product Title | Brand (e.g., “Adidas Gazelle Indoor Shoes – Orange | Adidas”)
Product Title | Category | Brand (e.g., “Gazelle Indoor Shoes | Women’s Shoes and Trainers | Adidas”)
CTA + Product Title | Brand (e.g., “Buy Gazelle Indoor Shoes | Adidas”)
CTA + Product Title | ISBN/Serial Number | Brand (e.g., “Buy Gazelle Indoor Shoes | 673-X-XX-XXXXXX-X | Adidas”)
For category pages, you can consider the following formats:
Category | Brands (e.g., “Women’s Shoes and Trainers | Adidas”)
CTA + Category | Brands (e.g., “Buy Women’s Shoes and Trainers | Adidas”)
Or, if you’re a local business with lots of different office or restaurant locations, you can use the following formats:
Restaurant Name, City – Town | Category | Brand (e.g., “Raffaello Ristorante, Los Angeles | Restaurant Reviews | TripAdvisor”)
Industry in City | CTA – Brand (e.g., “Plumbers in London – Get a Quote! | City Plumbers”)
So yeah, auto-generated title tags are a lifesaver for e-commerce websites with a massive number of product pages. With the right format and plugin, you can craft title tags that accurately describe your web pages and improve your SEO rankings.
Why is Google rewriting my title tags?
There have been instances known throughout the last couple of years that although you’ve poured your heart and soul into writing what you think is the perfect title tag, you end up seeing a complete different tag in the SERP. So what is that all about? Why does Google do this?
Well, according to some known Googlers, Gary Ilyses and Aaseesh Marina, there can be a couple of reasons:
1. Google thinks that your title tag isn’t great at all
We will never quit rewriting titles. We’ve seen so many sites whose title really suck. A lot of sites have no title; a lot of sites have a title saying “Top Page”. In fact, Google almost always rewrites titles. We couldn’t provide useful results to our users if we quit rewriting titles. Experiments showed us users preferred written titles. So, we’ll continue to write titles.
Gary Ilyses Google
This was the response from Gary in 2016. Google sees that not everyone has a perfect title matching the content on the page. Sometimes, there is no title tag at all. In cases like this, Google (re)writes a title tag for you
2. Google thinks there’s a more suitable title tag for a particular query
So the title tag is query dependent. Basically what we are trying to do is ensure that people will click on the results. We see lots of bad title tags [me: like homepage] yes and untitled for example, and I know for sure that this is actually a good thing, even if people don’t like it.
Gary Ilyses Google
Sometimes, Google sees your title, and it knows that if it just shakes up the words a little bit that the title matches the query better of the person searching. This is another example of Google sometimes rewriting your title tags to better answer the search query.
3. Google is looking at the anchor text of your inbound links to determine topic
If we see anchor text from website A linking to website B, sometimes we can pick, depending on the user’s query, sometimes we pick the anchor text that links from A to B as the title for that particular search result. Again, we obviously want to serve results that make the most sense for the users, users are what we try and make the best possible results for and in some cases if we think the anchor text is a good title, and it is more relevant for that particular query, then we’ll serve the anchor text.
Aaseesh Marina Google
Good to know. Google only does this when there is no other solution available (i.e., for pages that are currently indexed but blocked from being crawled by Googlebot).
When this happens, they look to outside factors (e.g., anchor text) is one of the only methods Google can use to write a good title tag.
How can I make stop Google from rewriting my title tags?
According to Gary, there is not much you can really do about this:
We also won’t provide ways to prevent rewriting entirely. We anticipate they can be abused. For example, keyword stuffing. […] Send us feedback that are on the bottom of search results pages if you don’t like rewritten titles.
Gary Ilyses Google
So the best thing to do is just follow the guidelines in the article and make the best title tag lines you can create in order for Google to not mess up your title tags.
There you have it, title tags aren’t rocket science, but you do need to invest a little bit more of your time into crafting them. Trust us, the extra time you spend on them now is really worth it when you see all those extra organic visitors coming in. Maybe even go back to some of your older publications and start updating those title tags too, and while you’re at it maybe even take a good look at the entire article and make them more relevant again, as updating your older content is one of the easiest ways to improve your site for SEO.